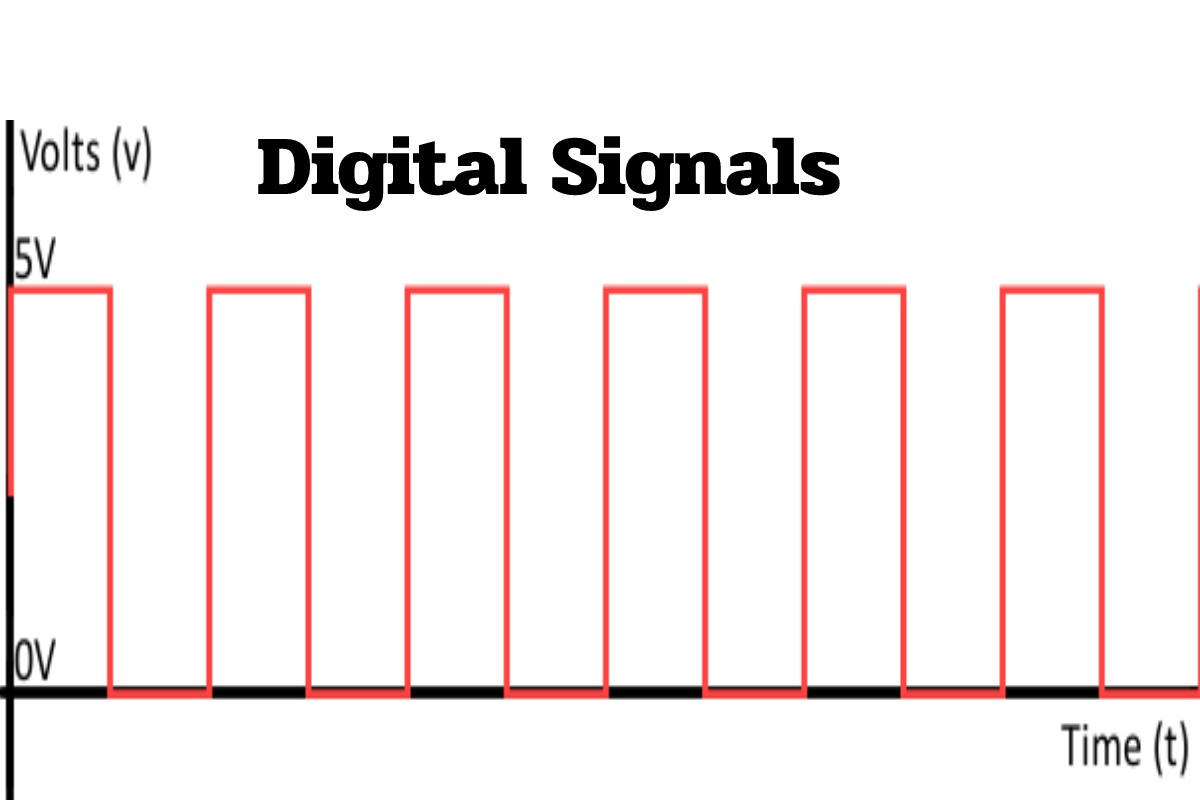
What is Digital Signals?
The digital signals are quantized discrete signals expressed in Bits (finite number of amplitudes). The binary logic used is (0,1) is determined in conjunction with the amplitude, which changes every second. “T = Time”. It contains electrical variables with two well-differentiated levels that alternate in time, transmitting information according to a previously agreed code. Each electrical level represents one of two symbols: 0 or 1.
Advantages of Digital Signals
The advantages of using digital signals, including digital signal processing (DSP) and communication systems, are as follows:
- It can transmit information with less noise, distortion and interference.
- Digital circuits can quickly reproduce in large quantities at relatively low costs.
- And also, digital signal processing is more supple because DSP operations can change using digitally programmable systems.
- Digital signal processing is more secure because digital information can easily encrypt and compressed.
- And also, digital systems are more precise, and the probability of errors can reduce by using error discovery and correction codes.
- Digital signals can easily store on any magnetic or optical medium using semiconductor chips.
- It can transmit over long distances.
Disadvantages of Digital Signals
The disadvantages of using digital signals, including digital signal processing (DSP) and communication systems, are:
- Higher bandwidth requires for digital communication compared to the analogue transmission of the same information.
- The DSP processes the signal at high speed and includes superior internal hardware resources. This results in higher power dissipation than analogue signal processing, which provides passive components that consume less power.
- Digital systems and processing are often more complex.
Characteristics of Digital Signals
These are the essential characteristics of digital signals.
- It is a continuous signal.
- This type of electronic signal can be processed and transmitted better compared to the analogue signal.
- They are versatile, which is why they widely use.
- The accuracy of the digital signal is better than that of the analogue signal.
Degradation and Restoration of Digital Signals
It used to transmit the bits also degrade, as any physical process degrades. However, this is the exciting part. The degraded signal can “clean up” because we know that each bit is 0 or 1. Therefore, the previous signal can be contaminated as follows:
- This restoration is not possible with analogue signals because with analogue. There are not only two possibilities. Comparison of a photocopy with a copy of a copy of a computer file. Computer files are (most likely) perfect copies of the original file.
- The actual implementation of digital transmission is a bit more complex than that, but the general technique is the same: two signals easily distinguishable even when degraded.
- Of course, at the other finish of the procedure, we have to change back to analogue, also called “reconstruction” of the signal. By drawing a curve through the points, the reconstructed curve dot does this in the following image.
- In the example, you can understand that the first share of the curve is correct, but there are errors in the last details.
The solution to this has two parts:
- The vertical axis must have a sufficiently satisfactory resolution not to have to round too much. The horizontal axis must be thin enough so that we can sample frequently enough.
- The example above decided that we did not often test sufficient to obtain the detail of the intervals.
- If we duplicate it, we get the following, which is much better.
- More acceptable resolution (bits on the vertical axis) and faster sampling gives you better quality (reproduction of original signal) but file size increases accordingly.
Examples of Digital Signals
Smart transmitters using various protocols transmit data through analogue and digital signals.
- Digital video signals.
- CD.
- DVD.
- The computer.
Difference between Analog and Digital Signals
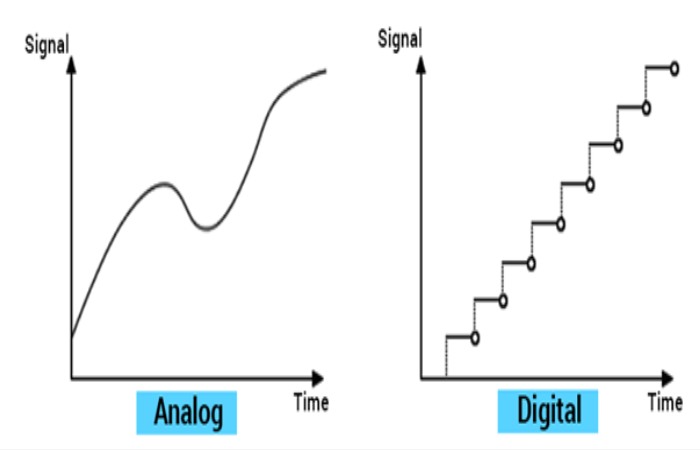
1. Analog signals
The analog signal is continuous and variable in time. Troubleshooting analog signals is complex. An analog signal is usually in the shape of a sine wave. They are easily affected by noise. Analog signals use continuous values to represent data. The accuracy of analog signals can be affected by noise. Analog signals can be affected during data transmission. Analog signals consume more power. Examples: measurements of temperature, pressure, flow, etc. Components like resistors, capacitors, inductors, and diodes used in analog circuits.
2. Digital signals
The digital signal has two or more states and in binary form. Troubleshooting digital signals are accessible. A digital signal is usually in the shape of a square wave. They are stable and less prone to noise. And also, it uses discrete values to represent data. The precision is immune to noise. They are not affected during data transmission. It uses less power. Examples: valve feedback, motor start, trip, etc. Components like transistors, logic gates, and microcontrollers used in digital circuits.
Conclusion
The digital signals have a discontinuous variation in time and can only take a limited number of discrete values. In fact, according to the RAE, DAM is a system that stores, digital means that it presents information through the use of discrete signals in the form of numbers or letters.
The parameters that define a digital signal are:
- Pulse height, directly related to the electrical level.
- Duration, which is the width of the pulse.
- Repetition rate, which is the number of times the pulse repeat per second.
- If we represent this digital signal in a coordinate system in which the abscissa axis is time, and the ordinate axis is the height of the pulse, the shape would be a typical square shape in which the vertical sides would be the pulse the horizontal sides the length of this.
Also Read: What is Cellular Data Plan? – Function, Advantages, and More