What is Data Processing?
Data processing occurs when data collect and translated into usable information. These are typically handled by data scientists, alone or in teams. It is important that processing is done correctly to not negatively affect the end product or the results obtained from the data. The end process of Data processing is the most crucial part which involves analyzing Data, For more knowledge, you can even consider the following Data analytics Course provided.
In the discipline of data science, R is the language that is most frequently used. The examination of both structured and unstructured data commonly makes use of it. As a result, R has emerged as the preferred language for performing statistical operations.You can learn R programming by R Programming Course to kick-start your Data Processing career.
Processing starts with data in its raw form. It converts it to a more readable format (graphics, documents, etc.), giving it the form and context necessary for computers to interpret and use for employees throughout an organization.
Stages of Data Processing
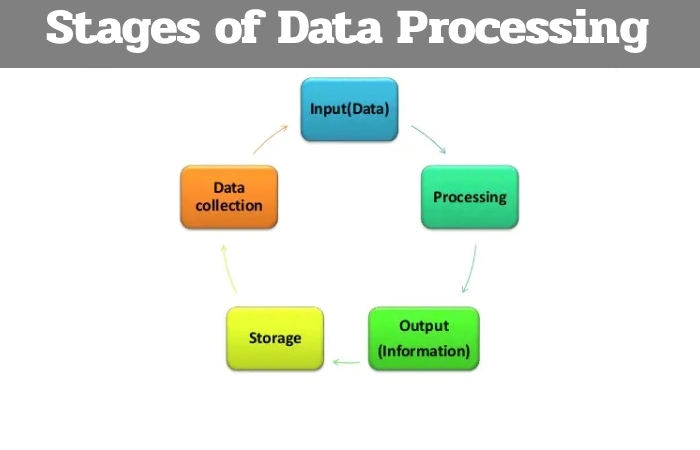
1. Data Collection
Data collection is the first processing step. And also, data is drawn from available sources, including data lakes and data warehouses. The available data sources must be reliable and well-created so that the data collected (which will later be used as information) is of the highest possible quality.
2. Data Preparation
Once the data is collected, the data preparation phase is carried out. Data preparation, often called “preprocessing,” is when the raw data is cleaned and organized for the next processing phase. During preparation, the raw data is diligently checked for errors. This step aims to eliminate bad data ( redundant, incomplete, or incorrect data) and create high-quality data for the best business intelligence.
3. Data Entry
The clean data is then fed to its destination (it can be a CRM, like Salesforce, or a data warehouse, like Redshift and translated into an understandable language. Data entry is the first step where the raw data begin to take shape as usable information.
4. Processing
During this phase, the data arrived into the computer in the previous phase process for interpretation. The processing is carried out utilizing machine learning algorithms. However, the process may vary slightly depending on the source of the data being processed (data lakes, social networks, connected devices, etc.) and its intention to use (study advertising patterns, medical diagnoses from connected devices, determine customer needs, etc.).
5. Data Output/Interpretation
The output/interpretation stage is the stage where the data is finally usable by non-data scientists. They translate, legible, and often presented in graphics, videos, images, plain text, etc. From that moment on, members of a company or institution can begin to self-manage the data for their own data analytics projects.
6. Data Storage
The last phase of data processing is storage. When all data process, it stores for future use. While there is some information that can use immediately, much of it will be useful later. In addition, properly storing our data is a necessity to comply with data protection legislation, such as the RGPD. When data well store, it is quick and easy for organization members to access it whenever they need it.
The Future of Data Processing
The future of data processing is in the cloud. Cloud technology takes advantage of the convenience of current electronic data processing methods and accelerates their speed and efficiency. If data is faster and higher quality, organizations have more data to use and more valuable information to extract.
With the migration of big data to the cloud, companies reap huge benefits. Big data technologies allow companies to combine all data management system into a single system that is easy to adapt to. As software changes and updates (as is often the case in big data), cloud technology seamlessly integrates the new with the old.
The benefits of data processing in the cloud are by no means exclusive to large corporations. In reality, small businesses can make even bigger profits. Cloud platforms can be inexpensive and offer the flexibility to grow and expand your capabilities as your business grows. It gives companies the ability to scale without paying a high price.
Elements of Data Processing
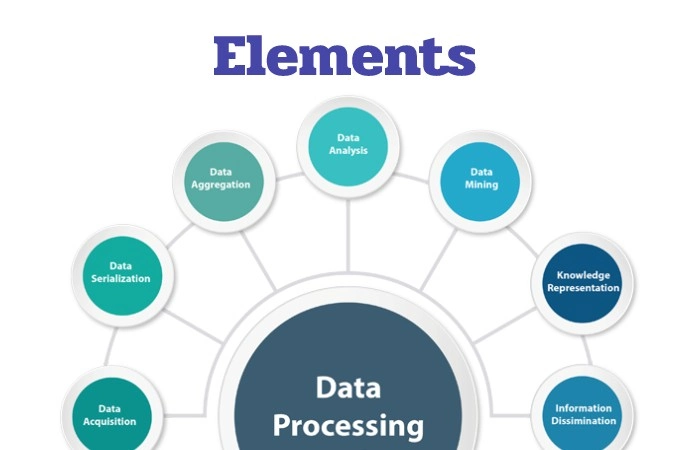
To process by a computer, the data first needs to convert into a machine-readable format. Once the data is in digital form, various procedures can apply to obtain useful information. Data processing can involve different processes, including:
- Data entry
- Capture Data
- Type of data
- Data cleaning
- Integrity Data
- Data encoding (encryption)
- Data transformation
- Translation Data
- And also, Data summaries
- Data aggregation
- Validation Data
- Data modeling
- Data analysis
- Statistical data analysis
- Data visualization
- Storage Data
- Data mining
- And also, Data interpretation.
Analytics of Data Processing
Big data is changing the way businesses do business, and for companies of any size, gaining a competitive advantage requires a robust data processing strategy. Although the six phases of data processing will not change, the cloud has led to great technological advances over time, becoming today the most advanced, profitable, and fastest method.
What happens from now on? It’s time to put your information to work. When your data processed, it can effectively analyze for business intelligence. With the help of data analytics, they will be able to make faster and smarter business decisions. Also, get started, take a look at the Talend Best Practice Report: Making Analytics Effective and Integrating for Practical Use.
Operations in the Data Processing

1. Registration
It has to do with transferring data to some form of standardized document throughout the processing cycle. For example, a teacher writes down on his list the points obtained by the students, and at the end of the semester, he calculates the final marks and writes them down on his list. He receives a certificate and places the final grades there, records them on the student’s grade sheet, and then delivers the minutes to the respective office.
2. Duplication
It consists of reproducing the data in many documents or forms. Example: A report can record by typing it while making carbon copies. In another case, enter it into the computer, then print and photocopy the document.
3. Verification
It consists of carefully checking the data to avoid any errors. Example: Typewritten reports can be re-read for correction.
4. Separation
The data separated into several categories. For example, a group of questionnaires for students can separate according to gender or courses.
5. Classification
In organizing the data in a specific order. For example, the names in the phone list have sort in alphabetical order. In this case, the data classify without separating. Sorting can also do after separation.
Another example: an employee log file contains name, social security number, and place of employment. If the file needs to sort according to the alphabetical order of the names, the “name field” is called “KEY”.
6. Intercalation
Two or more data sets that have classifies with the same key take and summarized to form a single data set: For example, Two packages of cards classified numerically, the same ones that interleave and archived in the combined package during the passing of the cards. And also, if the cards have a similar number, a sub-rule determines which one should fill. When one pack is empty, the other cards place at the end of the combo pack.
7. Calculation
The word calculation refers to the computation, account, or investigation made of something through mathematical operations. And also, the concept also uses synonymously with conjecture. And also, it is the execution of numerical calculations on the data.
8. Recovery
And also, data recovery refers to the techniques used to recover files that have to lose or deleted from a storage medium.
Conclusion
It may or may not distinguish from data conversion, which involves changing data into another format and does not include any data manipulation. During processing, raw data uses to input crop information as an output, usually in reports and other analytical tools.
Also Read: Artificial Intelligence – Definition, Important, Types, and More