M2M Definition
M2M is precisely what it sounds like two machines “communicating” or exchanging data, with no human interaction or interface. This includes serial connection, power line connection (PLC), or wireless communications over the Industrial Internet of Things (IoT). The switch to wireless technology has made Machine to machine communication much easier and more connected to applications.
In general, when someone talks about M2M communication, they are often referring to cellular communication for in-vehicle plans. Examples of M2M communication, in this situation, would be ATMs that send inventory information or ATMs that get permission to dispense cash.
As companies realize the value of M2M, it has acquired a new name: the Internet of Things (IoT). IoT and M2M have similar promises: fundamentally change the way the world works. Like IoT, M2M allows almost any sensor to communicate, opening the possibility for systems to control themselves.
And automatically respond to changes in the environment, with much less human intervention. M2M and IoT are almost identical; the exception is IoT (the newer term) which generally refers to wireless communications, while M2M can refer to two machines, wired or wireless, communicating with each other.
How does M2M Works?
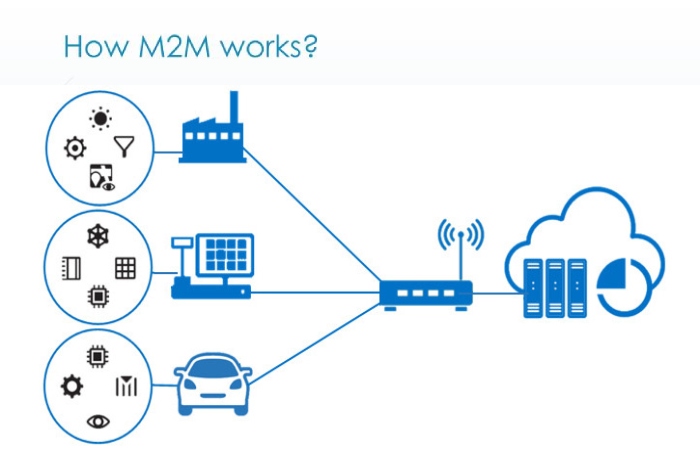
As stated earlier, machine-to-machine communication makes the Internet of Things possible. M2M is among the fastest-growing kinds of connected device technologies on the market today. According to Forbes, in large part, M2M technologies can connect millions of devices within one network. The range of connected devices includes everything from vending machines and medical equipment, including vehicles and buildings. Almost anything that contains sensors or control technology can connect to some wireless network.
It sounds complex, but the thought behind the idea is quite simple. Essentially, M2M networks are very similar to LANs or WANs. But they use exclusively to allow machines, sensors, and controls to communicate. These devices transmit the information they collect to other devices on the network. This process enables a human (or intelligent control unit) to assess what is going on in the network and issue the appropriate instructions to member devices.
What are the Applications of M2M?

The possibilities in M2M can see in four main use cases, which we detail below:
1. Manufacturing
Whether it’s food processing or overall product manufacturing, every manufacturing setting relies on technology to safeguard costs appropriately manage and processes execute efficiently. Automating manufacturing processes in such a fast-paced environment is expected to improve processes further. In the manufacturing world, this could include highly automated equipment maintenance and safety procedures.
For example, M2M tools let business owners receive alerts on their smartphones when critical equipment needs repair to fix issues as they arise. Sophisticated sensor networks connected to the Internet could even automatically order spare parts.
2. Household Appliances
The IoT is already affecting the connectivity of home devices through platforms like Nest. However, M2M expects to take the IoT home to the next level. Manufacturers like LG and Samsung are already gradually introducing intelligent appliances to help ensure a better quality of life for occupants.
For example, an M2M-enabled washing machine could send alerts to owners’ smart devices once it’s finished washing or drying. And a smart refrigerator could automatically order food from Amazon once it’s finished. There are many other examples of home automation that can potentially improve the quality of life for residents.
It including systems that allow household members to control HVAC systems using their mobile devices remotely. In situations where a homeowner chooses to leave work early, he can communicate with the home’s heating system before leaving the job to make sure the temperature in the house is comfortable when he arrives.
3. Management of Health Devices
One of the most significant changes for M2M technology is healthcare. With M2M technology, hospitals can automate procedures to ensure the highest levels of treatment. The use of devices capable of reacting faster than a healthcare professional in an emergency makes this possible.
For example, when a patient’s vital signs drop below normal, an M2M-connected rescuer could automatically deliver oxygen and additional care until a healthcare professional arrives on the premises.
M2M also allows patients to be tracked in their homes rather than in hospitals or care facilities. For example, devices that follow the regular movements of a frail or older person can detect when they have had a fall and alert a healthcare professional to the situation. Another use case in healthcare would be advantage tracking. Locating equipment rapidly can mean life or death in a hospital.
4. Intelligent Management of Profits
In the new age of energy competence, automation will quickly become the new normal. As energy companies seek new ways to automate the metering process. M2M comes to the rescue, helping energy companies automatically collect energy usage data, so they can accurately bill customers.
Smart meters can track the amount of energy used by a home or business and automatically alert the energy company, replacing sending an employee to read the meter. Or requiring the customer to provide a reading. This is even more important as values move toward more dynamic pricing models, charging customers more for energy use during peak hours.
Some fundamental analysts predict that soon all objects or devices should be able to connect to the cloud. It’s a bold but seemingly accurate declaration. As more customers, users, and business owners demand deeper connectivity, technology must continually equip to meet the needs and challenges of tomorrow.
This will enable a wide range of highly automated processes, from equipment repairs and firmware updates to system diagnostics, data recovery, and analysis. Information will be delivered to critical users, engineers, data scientists, and decision-makers in real-time, eliminating the need for guesswork.
The Value of M2M

The growth of M2M and IoT markets has increased rapidly, and, according to many reports, the change will continue. Strategy Analytics estimates that LPWAN (Low Power Wide Area Network) connections will grow from 11 million in 2014 to 5 billion in 2022. And IDC says the global market for IoT solutions will grow from $ 1.9 trillion in 2013 to $ 7.1 trillion in 2013. dollars in 2020.
Many large mobile operators, such as AT&T and Verizon, see this potential and implement their own M2M platforms. Intel, PTC, and Wipro are trading heavily in M2M and striving to capitalize on this significant industry growth momentum. But there is still an excellent opportunity for new technology companies to engage in highly automated solutions to help streamline processes in almost any type of industry. We are confident that we will see a significant influx of companies innovate in this area over the next five years.
However, as the cost of M2M communication lasts to drop, businesses must determine how they will create value for companies and customers. In our mind, the opportunity and value of M2M do not lie in the more traditional layers of the communication world. Cell operators and hardware manufacturers, for example, are starting to look for comprehensive offerings that enable M2M and IoT product development. We firmly believe that the value lies on the application side. And intelligent applications will now drive the growth of this industry.
Conclusion
Businesses shouldn’t think of IoT orM2M for IoT or M2M. Instead, they should focus on optimizing their business models or delivering new value to their customers. For example, if you are a logistics company like FedEx or UPS, you have apparent options for automated logistics decisions that machines make. But if you’re a retailer, the transition to automation might not be that easy.
One thing to think of is a ‘cool’ automated process, for example, creating an advertisement that automatically links to a specific customer using M2M technology. Still, before proceeding with the process, you need to consider the value that you get out of it. How much does it cost to implement? Are you going to target the right audience? Will it be effective?
Any company considering entering the IoT space needs to understand its business model and generate money. And how it will deliver value to customers or internal processes.
Also Read: A Comparison of Wise or N26 as FinTech Account