What is Software?
The term software is an English word taken by other languages. It designates any intangible (and not physical) component that is part of devices such as computers, mobile phones, or tablets, allowing their document management.
It makes up of applications and programs designed to fulfill various functions within a system. In addition, it is made up of user information and processed data.
A part of the software tells the hardware (the physical aspect of a device) by instructions and steps.
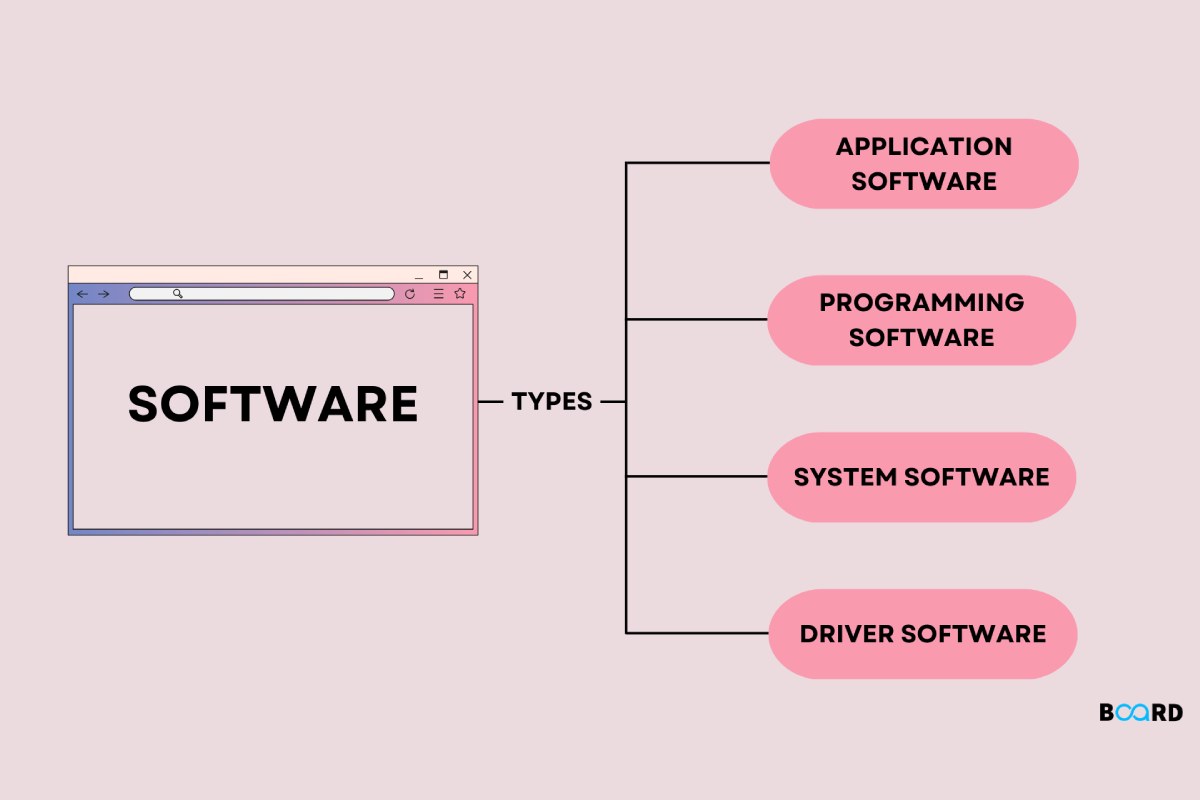
Types of Software
The software classifies according to its function:
System software: Programs that allow the user to interact with the system to exercise control over the hardware. The system software also provides support for other programs—for example, operating systems or servers.
Programming software: Programs design as tools that allow a programmer to develop computer programs. They use techniques and a specific programming language—for example, compiling a program or multimedia editors.
Application software: Programs designed to perform one or more specific tasks simultaneously can be automatic or assisted, for example, video games or media players.
Examples of Software
There are many examples of software, which classify according to their function in:
Image Editing: For example, Adobe Photoshop, Paintshop, GIMP.
Word Processor: For example, Microsoft Word, Word Pad, Notepad.
Audio: For instance, Adobe Audition, Abelton, Pro Tools.
Communication: For example, Facebook, Skype, Zoom.
Design and Architecture: For example, AutoCAD, Adobe Illustrator, Revit.
Accounting: For example, Logger, Xero, Nubox.
Operating System: For instance: Linus, macOS, Windows.
Virus Protection: For example, AVG Antivirus, McAfee, Panda.
Programming: For example, Microsoft Visual Studio, Xcode, Lazarus.
How is the Software Written?
The basic form of the first software was binary code. This is a numbering system in which there are only two numbers: 0 and 1. Currently, programmers and software engineers write in programming languages, known as C ++, Ada, R, and JavaScript.
Importance of Software
Nowadays, it uses to control practically any electronic device. They find in the control systems of airplanes, transportation, and power plants. Also, in electronic appliances that we frequently use, such as ovens, microwaves, television, and refrigerators.
Medical equipment such as pacemakers and diagnostic equipment are also controlled by software. In short, modern society is contingent on its correct operative.
Software Engineering
It refers to applying engineering principles in software construction: development, operation, and maintenance. The professional in charge of this task is known as a system engineer.
Let’s make the similarity between a programmer and a system engineer. A programmer inscribes an entire program as a custom activity. Instead, a system engineer writes a piece of it combined with others to build a system as part of a team effort.
Functions of Software
As this description is so broad, there are many elements within a Computer System that we could call, so their differentiation is common. One of the most common and widespread differentiation methods carry out as a result of the function of each program in a computer system; namely:
- It is a very low-level program, not intended for the user to interact with it, and controls the electronic circuits of our equipment.
- It is essential to recognize hardware in a computer and find it in many ways; one of the most common forms that we can see is the BIOS of our system (to which we dedicate its text).
- Operating system. Windows 8 and Windows 10 are the most widely used operating systems today. They are a set of programs in charge of management software is a system’s hardware and provides an interface to communicate with the end-user of said system.
- They intend to solve the problems raised by the users of a plan directly. Adobe Photoshop could be an application example.
- Along with the operating system, it is the type of program with which most users interact.
- Its function is to perform background tasks to facilitate the operation of other programs; they are an intermediate medium, and users do not have to interact directly with them.
Conclusion
The software embeds part of an electronic device and is used to control the functions of the physical characteristics of the computer—for example, television sets, airplanes, and video games. When an operator journalists a button on the aircraft controls command, it performs the corresponding function.
It characterizes because of its design according to the electronic equipment. For example, when we press the microwave keypad to heat for two minutes at high power, the embedded system commands the microwave to operate at maximum voltage and turn off after a specific time.